Nature Communications: Mitochondrial dynamics controls antitumor innate immunity by regulating CHIP-IRF1 axis stability
Zhengjun Gao, Yiyuan Li, Fei Wang, Tao Huang, Keqi Fan, Yu Zhang, Jiangyan Zhong, Qian Cao, Tong Chao, Junling Jia, Shuo Yang, Long Zhang, Yichuan Xiao, Ji-Yong Zhou, Xin-Hua Feng, and Jin Jin
Nature Communications, 2017 Nov 27;8(1):1805.
Abstract
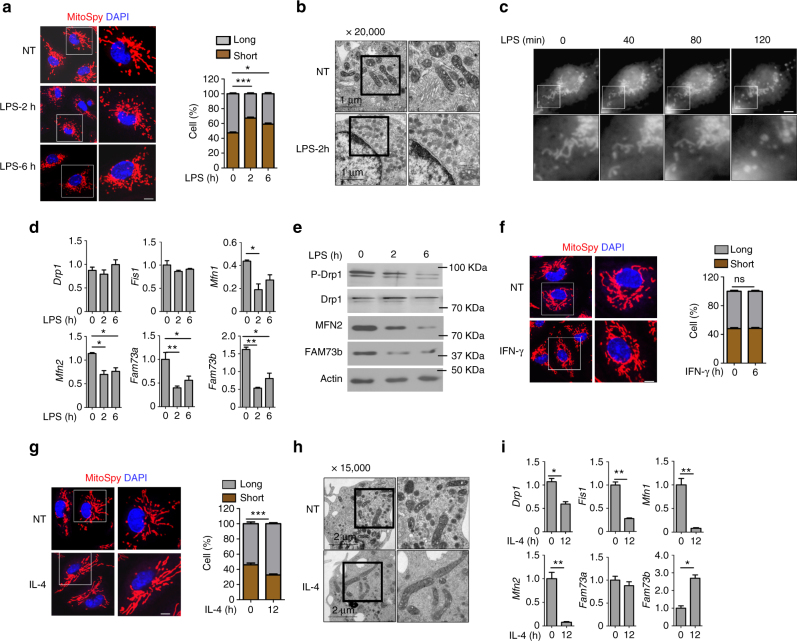
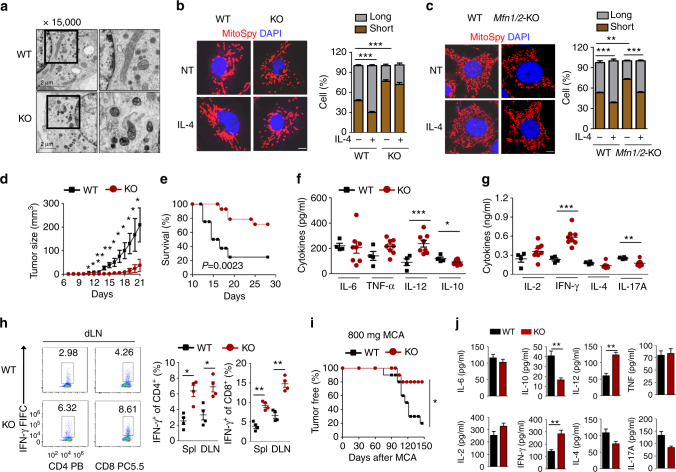
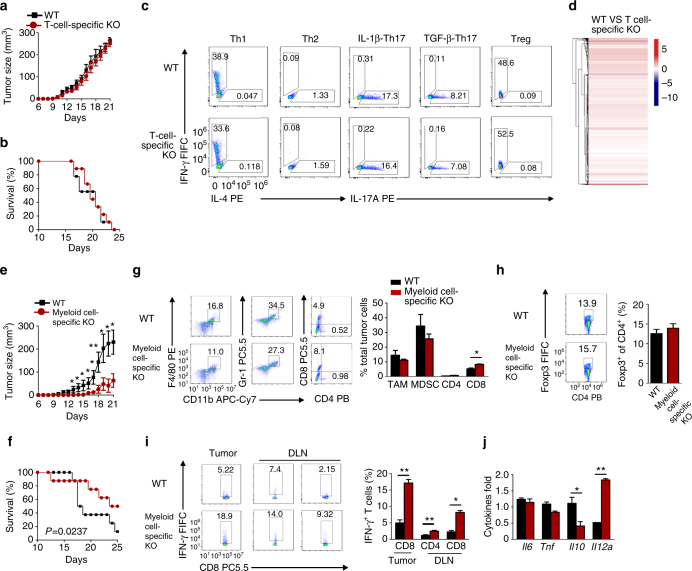
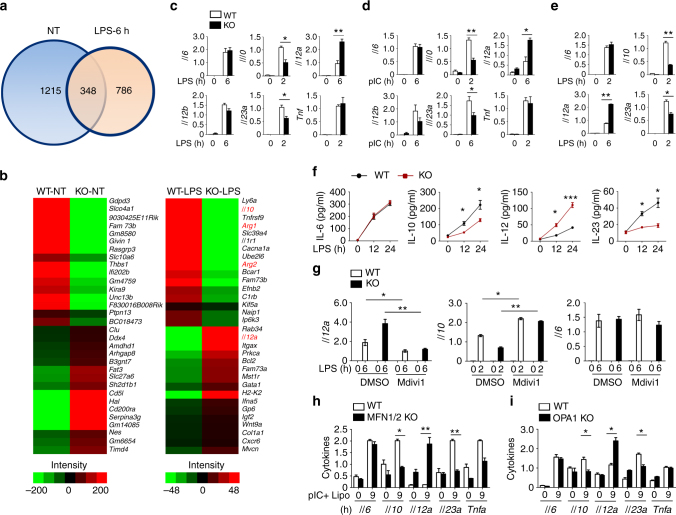
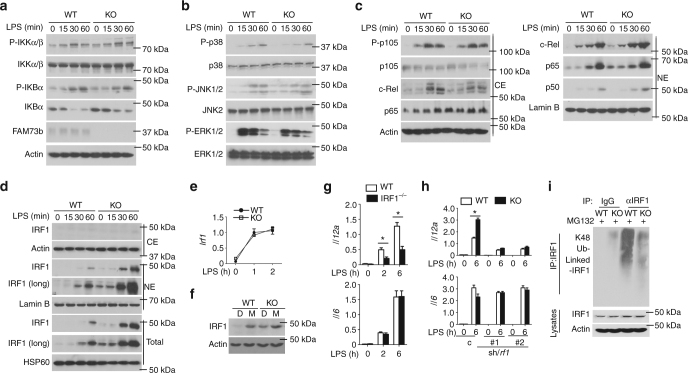
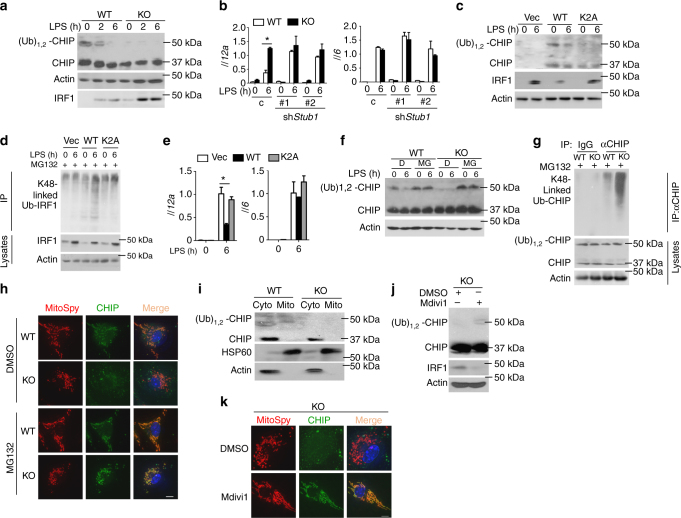
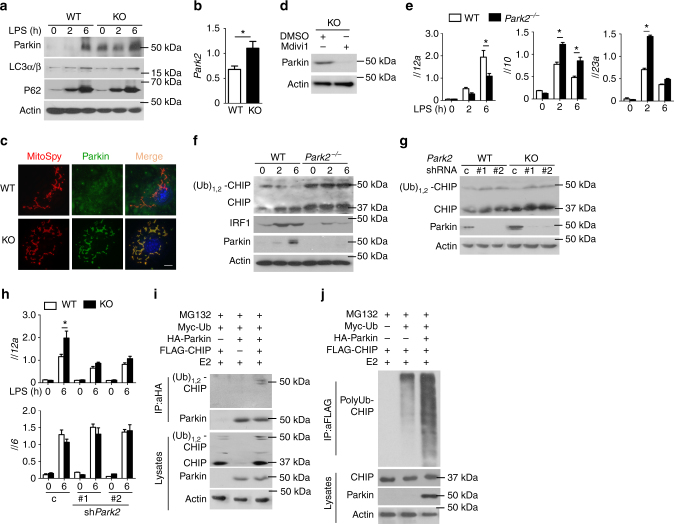
Macrophages, dendritic cells and other innate immune cells are involved in inflammation and host defense against infection. Metabolic shifts in mitochondrial dynamics may be involved in Toll-like receptor agonist-mediated inflammatory responses and immune cell polarization. However, whether the mitochondrial morphology in myeloid immune cells affects anti-tumor immunity is unclear. Here we show that FAM73b, a mitochondrial outer membrane protein, has a pivotal function in Toll-like receptor-regulated mitochondrial morphology switching from fusion to fission. Switching to mitochondrial fission via ablation of Fam73b (also known as Miga2) promotes IL-12 production. In tumor-associated macrophages, this switch results in T-cell activation and enhances anti-tumor immunity. We also show that the mitochondrial morphology affects Parkin expression and its recruitment to mitochondria. Parkin controls the stability of the downstream CHIP–IRF1 axis through proteolysis. Our findings identify mechanisms associated with mitochondrial dynamics that control anti-tumor immune responses and that are potential targets for cancer immunotherapy.